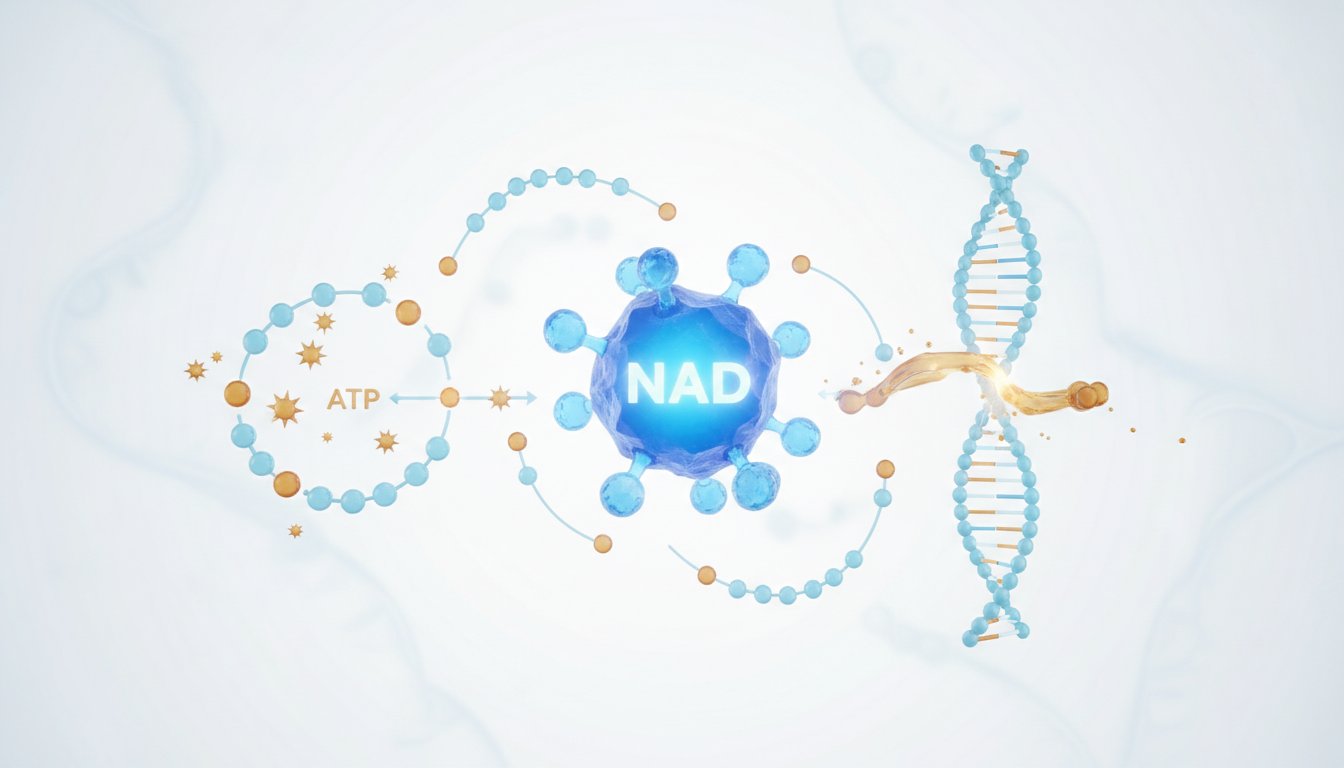
Boosting NAD Levels Enhances Cellular Health and Healthspan
TL;DR
- Declining NAD levels are directly associated with aging and metabolic stress, impacting cellular energy production, DNA repair, and cell death processes, suggesting a causal link to age-related dysfunction.
- Elevating NAD levels via precursors like NR enhances mitochondrial function and biogenesis, potentially improving cellular energy yield without increasing caloric intake, supporting healthspan.
- NAD plays a critical role in DNA repair mechanisms, and its depletion under stress or damage impairs the cell's ability to flag and heal mutations or oxidative stress.
- While NAD levels decline with age, blood NAD levels are not a reliable biomarker for biological age due to daily fluctuations and organ-specific variations, making tissue-level assessment crucial.
- Animal studies consistently demonstrate that elevated NAD levels can prevent or treat age-related conditions, with emerging human studies showing promise in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's.
- NAD precursors like NR are more effective than NAD itself for cellular uptake, as NAD is a large molecule that struggles to enter cells, potentially causing inflammation when administered directly.
- NAD elevation may offer benefits for fatigue and brain fog associated with conditions like Long COVID, as evidenced by small studies showing improvement after NR supplementation.
- NAD's role in cellular resilience and energy metabolism suggests potential applications beyond disease treatment, including cosmetics and beverages, due to its safety profile and ability to boost mitochondrial function.
Deep Dive
The core argument is that Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), a molecule vital for cellular energy and repair, declines with age and stress, and boosting its levels through precursors like Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) can enhance cellular health and potentially extend healthspan. This has significant implications for understanding aging as a process of accumulated damage and for developing interventions that support the body's natural repair mechanisms, moving beyond symptom management to cellular resilience.
NAD plays a critical role in two primary cellular functions: energy production within mitochondria and DNA repair through enzymes like PARP. As NAD levels naturally decrease with age, beginning in one's twenties, cellular functions become less efficient. This decline is exacerbated by metabolic stress, inflammation, and damage. The direct relationship between NAD levels and aging is observed in rare progeroid syndromes where individuals experience rapid aging and have undetectable NAD levels. While the exact causal link--whether NAD depletion causes aging dysfunction or is a consequence of cellular repair efforts--remains an area of research, increasing NAD levels demonstrably improves cellular performance. Unlike telomeres, which are a specific biomarker but difficult to manipulate therapeutically, NAD's role is more dynamic and tied to ongoing cellular processes, making it a critical factor in healthspan rather than a simple aging clock.
Research, particularly in animal models, indicates that elevating NAD levels can prevent or treat age-related conditions. Human studies, including those on Parkinson's disease, have shown promising secondary outcomes related to motor function and safety, with larger trials underway. The podcast clarifies that while NAD itself is not bioavailable orally or via injection due to its large molecule size and breakdown, precursors like NR are efficiently converted to NAD within cells. NR is particularly notable for its ability to specifically target cells under metabolic stress, making it a rational and safe approach to boosting NAD. This contrasts with direct NAD supplementation, which is often ineffective and can cause side effects. The implications extend to potential applications in cosmetics and as a complementary therapy in pharmaceutical interventions for a range of diseases, including neuroinflammatory conditions and fatigue associated with Long COVID, where small studies have shown positive results with NR supplementation.
The discussion also highlights broader issues within the dietary supplement industry, emphasizing the lack of transparency and the prevalence of misinformation. The effectiveness of many supplements is questioned due to poor bioavailability or the discrepancy between label claims and actual product content, a problem exacerbated by low entry barriers and limited regulatory oversight. This underscores the importance of rigorous scientific research and reputable manufacturers that adhere to quality controls and provide transparent data. The future of NAD research points towards a deeper understanding of its role in promoting self-healing mechanisms within the body, potentially leading to more effective interventions for age-related decline and disease, repositioning NAD as a fundamental component of cellular health and longevity.
Action Items
- Audit NAD+ precursors: Evaluate 3-5 NAD+ precursor supplements for bioavailability and safety (ref: Charles Brenner's research).
- Implement NAD+ precursor supplementation: Take 1 gram of Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) daily for 3 months to assess impact on cellular resilience and energy.
- Track health metrics: Measure workout recovery rate and sleep quality before and after 3 months of NR supplementation to quantify benefits.
- Investigate NAD+ IV therapy: Compare efficacy and side effects of NR injections versus NAD+ IV infusions across 2-3 clinics.
Key Quotes
"NAD is very exciting. It stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. It's a coenzyme that's found in all living cells, plant and animal, and it's vital to all key metabolic processes within that cell. We make energy inside the cell; it's not made outside the cell. There are these organelles called mitochondria which take oxygen from air that we breathe and nutrients from food that we eat and they put it through something that we've called the Krebs cycle and the yield of that process is something called ATP, these molecules that are filled with energy that transfer throughout the cell. NAD is at every step along the way in that conversion process of taking oxygen and nutrients and converting it into ATP."
Robert Fried explains that NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a crucial coenzyme present in all living cells. Fried highlights its fundamental role in cellular energy production, specifically within mitochondria, where it facilitates the conversion of oxygen and nutrients into ATP, the cell's energy currency. This process underscores NAD's importance for basic cellular function and survival.
"And NAD even goes beyond mitochondrial health. There are mechanisms in place within the cell for healing when there is damage. There are these enzymes called PARP enzymes where where there's a gene mutation or there's some physical damage or there's oxidative stress or inflammation, these one group of PARP enzymes will flag it and another group of PARP enzymes will try to heal it or cure it and then even another group if the cell is irreparable will actually do something called apoptosis, kill the cell. All those processes are related to NAD."
Robert Fried elaborates on NAD's functions beyond energy production, detailing its involvement in cellular repair mechanisms. Fried explains that NAD is essential for PARP enzymes, which detect and attempt to fix DNA damage, inflammation, or oxidative stress. He notes that NAD also plays a role in apoptosis, the programmed cell death of irreparable cells, demonstrating its broad impact on cellular health and maintenance.
"The levels of NAD that we have decline fairly rapidly, even beginning in your 20s. But what we've seen is that when a cell is under metabolic stress of any type, that's when NAD levels go down. Interestingly, there are these whole sets of orphan diseases, meaning rare diseases, that where kids age very very rapidly. There's several of them we studied all of them, progeria is that one of them, that's an example of a point Cockayne syndrome is another example of one, ataxia, where these kids age very rapidly and some of them, they actually die of old age at the age of 12 or 13. What we've seen in some of these conditions is non-detectable levels of NAD."
Robert Fried discusses the relationship between NAD levels and aging, stating that NAD naturally declines with age, starting in one's 20s. Fried points out that metabolic stress further reduces NAD levels. He connects this to rare diseases like progeria and Cockayne syndrome, where individuals experience rapid aging and often have undetectable NAD levels, suggesting a direct link between NAD and the aging process.
"The thing about NAD is it sort of varies over time, even during the day and even organ to organ. Most people are measuring their blood NAD levels these days. Blood NAD levels isn't really a great indicator of how high your NAD levels are. You're where you have a damaged cell is where you're likely to have a diminished NAD level. It's very difficult to do that in a kidney, you have to get a biopsy. Right. There are ways to measure NAD in a brain with an MRI without actually non-invasively, but we don't really have good consistent easy ways to measure NAD levels in the tissue and it varies and of course almost almost like cholesterol, you know, in the course of the day it could go up, it could go down."
Robert Fried explains the challenges in accurately measuring NAD levels, noting that they fluctuate throughout the day and vary between organs. Fried states that blood NAD tests are not a reliable indicator of NAD levels in damaged cells, where deficiencies are most critical. He highlights the difficulty in obtaining tissue-specific NAD measurements and suggests that NAD levels can change similarly to cholesterol, influenced by daily activities and stress.
"So NAD was initially discovered in something like 1906. Researchers were investigating fermentation in yeast and they realized that there was this coenzyme that was involved in the energy metabolism process. Then in like the 1930s, there was this outbreak of a condition called progeria and they found out that they could cure this disease with vitamin B3. Uh, and that and that vitamin B3 elevated NAD and by elevating NAD, they're able to cure progeria. And niacin, B3 is niacin, right? Yeah. So niacin increases NAD. There are several molecules that increase NAD. Nicotinamide riboside or Nigen is not the only one. It just happens to be the best one, but it's not the only one."
Robert Fried traces the historical discovery of NAD, beginning with its identification in yeast in 1906 and its role in energy metabolism. Fried recounts how vitamin B3 (niacin) was found to cure progeria by elevating NAD levels in the 1930s. He clarifies that while niacin increases NAD, nicotinamide riboside (NR), also known as Nigen, is presented as a more effective precursor for boosting NAD.
"So NR is amazing in that it not only safely and efficiently elevates NAD, but it specifically does it in the cells that are the most damaged. Wow. Interesting, right? So people say to me all the time, what can I expect if I start taking True Niagen? And my answer is, what's broken? What worked better 10 years ago? Could it be your elbow pain? Could it be recovery from workouts? Could it be your sleep level? Retrieval, cognition? Something like this."
Robert Fried emphasizes the unique benefits of NR (nicotinamide riboside) by explaining that it not only safely and efficiently increases NAD levels but also targets cells that are most damaged. Fried suggests that individuals taking NR should consider what physical or cognitive functions were better in the past, as these are the areas where improvements might be most noticeable. This highlights NR's potential to address specific cellular issues and restore function.
"Why would you say it's uh not smart to take NAD? Because I know it's kind of trendy. I don't know if trendy is the right word, but people are doing it at least here in LA and they always say it makes them feel sick. Every one of them, it makes them feel sick and they sweat and they have headaches. Today, there are zero studies and I spent a lot of time reading studies that we know of that show that taking NAD elevates NAD. NAD is not bioavailable. It's a very large molecule and it's a nucleotide, meaning there's a phosphate group on the perimeter of it. It cannot enter cells."
Robert Fried advises against taking NAD directly, noting that it
Resources
External Resources
Books
- "The Singularity Is Near" by Ray Kurzweil - Mentioned as a book discussing pursuits to extend life, particularly through data-oriented and information technology approaches.
Articles & Papers
- "White papers" by Brunie Feldin - Mentioned as demonstrating that nicotinamide riboside and other vitamin B3s have more anti-cancer properties than pro-cancer properties.
People
- Robert Fried - CEO of TrueNigen, discussed for his background in Hollywood and transition to the longevity science industry, focusing on NAD and NR.
- Charles Brenner - Mentioned for his discovery that nicotinamide riboside efficiently elevates NAD levels and for having been a guest on the podcast twice.
- Roger Kornberg - Mentioned as a Nobel Prize winner in chemistry at Stanford and the son of Arthur Kornberg.
- Arthur Kornberg - Mentioned as a Nobel Prize winner and the father of Roger Kornberg, who discovered NAD's centrality to the Krebs cycle.
- Bruce German - Mentioned as the head of life sciences at UC Davis and a world-leading expert on milk, who is on TrueNigen's scientific advisory board.
- Brunie Feldin - Mentioned as a leading cancer researcher at Scripps Research Institute and a scientific advisor for TrueNigen.
- Ray Kurzweil - Mentioned for his books "The Singularity Is Near" and its follow-up, discussing longevity pursuits and the concept of uploading consciousness.
- Dr. Anurag Singh - Mentioned as the Chief Medical Officer at Timeline, who was interviewed on episode 418 of the show regarding Mitopure.
Organizations & Institutions
- TrueNigen - Mentioned as a company focused on NAD and longevity science, with Robert Fried as CEO.
- Columbia Pictures - Mentioned as a studio where Robert Fried worked in the 1980s, introducing spreadsheet analysis into its business operations.
- Sony - Mentioned as the acquirer of Columbia Pictures.
- Gates Foundation - Mentioned in relation to Charles Brenner's studies on how elevating NR increases mother's milk production.
- Timeline Nutrition - Mentioned as the company behind Mitopure gummies.
- Nigen Bioscience - Mentioned as the former name of Chromadex, which Robert Fried began buying stock in in 2013 and joined the board of in 2015.
- UC Davis - Mentioned as the institution where Bruce German heads life sciences.
- Scripps Research Institute - Mentioned as the institution where Brunie Feldin is a leading cancer researcher.
- Harvard - Mentioned in relation to researchers at Mass General Harvard who approached TrueNigen about a long COVID study.
- Mass General - Mentioned in relation to researchers at Mass General Harvard who approached TrueNigen about a long COVID study.
- FDA - Mentioned as having a small budget and limited capacity to oversee the thousands of companies in the dietary supplement space.
- FTC - Mentioned as an entity with limited capacity to oversee the dietary supplement industry.
- NSF - Mentioned as a legitimate entity providing certification, particularly for professional athletes.
- Alchemist - Mentioned as a company that provides a label for measuring whether what's on the label is in the bottle.
- The Trust Alliance - Mentioned as an alliance being created by TrueNigen to foster trust among influencers, retailers, and supplement companies.
- Nigen Labs - Mentioned as the labs where researchers work on ingredients for TrueNigen.
Websites & Online Resources
- TrueNigen.com - Mentioned as the website for TrueNigen, with a promo code "genius20" for a discount.
- cbdistillary.com - Mentioned as the website for CB Distillary, with a promo code "max" for a discount.
- timeline.com/max - Mentioned as the website to get 20% off Mitopure gummies.
- aboutnad.com - Mentioned as an objective website listing research in the NAD space, without promoting products.
- Nigenplus.com - Mentioned as a website to find a store locator for clinics offering NAD injections or IVs.
- Nigenbioscience.com - Mentioned as the corporate website for Nigen Bioscience.
- maxlugavere.com/newsletter - Mentioned as the website to sign up for a free weekly newsletter.
Other Resources
- NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) - Mentioned as a coenzyme vital to cellular energy, mitochondrial function, and DNA repair.
- NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) - Mentioned as a supplement and precursor that boosts NAD levels, particularly in damaged cells.
- Mitochondrial Health - Discussed as a key area related to NAD function and cellular energy production.
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction - Mentioned as a condition associated with aging and cellular decline.
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) - Mentioned as energy-filled molecules produced by mitochondria.
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) - Mentioned as a process within mitochondria that yields ATP.
- PARP Enzymes - Mentioned as enzymes involved in cell repair and apoptosis, dependent on NAD levels.
- Apoptosis - Mentioned as the programmed cell death process.
- Progeria - Mentioned as a rare disease where children age rapidly, with non-detectable NAD levels observed in some cases.
- Pontocerebellar Hypoplasia - Mentioned as a rare disease where children age rapidly.
- Ataxia - Mentioned as a rare disease where children age rapidly.
- Telomeres - Mentioned as a biomarker of aging, with research showing correlation to age but not yet a method to prevent or reverse aging by elongating them.
- Mice Studies - Mentioned as having shown that aging conditions are associated with reduced NAD levels and that elevating NAD helps prevent or treat disease.
- Rat Studies - Mentioned as having shown that elevating NAD helps prevent or treat disease.
- Pig Studies - Mentioned as having shown that elevating NAD helps prevent or treat disease.
- Dog Studies - Mentioned as having shown that elevating NAD helps prevent or treat disease.
- Parkinson's Disease - Discussed as a condition potentially related to mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation, with studies on NR showing improvements in markers.
- Alzheimer's Disease - Mentioned as a condition related to neuroinflammation.
- Substantia Nigra - Mentioned as a region of the brain where dopamine-producing neurons are affected in Parkinson's disease.
- CBD (Cannabidiol) - Mentioned as a compound from CB Distillary that supports relaxation and sleep.
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) - Mentioned as a compound from CB Distillary used in sleep gummies.
- CBN (Cannabinol) - Mentioned as a compound from CB Distillary used in sleep gummies.
- Mitopure Gummies - Mentioned as a product powered by urolithin A to support mitochondrial health.
- Urolithin A - Mentioned as a clinically studied compound that supports mitochondrial health by activating mitophagy.
- Mitophagy - Mentioned as the body's natural process for clearing out old, dysfunctional mitochondria.
- Environmental Toxicants - Discussed as potential contributors to Parkinson's disease, possibly by affecting cell resilience.
- Vitamin B3 - Mentioned as a precursor that elevates NAD, with niacin being a form of it.
- Niacin - Mentioned as a form of Vitamin B3 that elevates NAD but can cause flushing and is less efficient than NR.
- NR Kinase Pathway - Mentioned as a pathway discovered by Charles Brenner that is activated under specific metabolic stress to call for NR.
- Pharmaceutical Grade NR - Mentioned as a requirement for injections or IVs, which TrueNigen has made available.
- Liposomal Formulations - Mentioned as a method to improve bioavailability of certain compounds like glutathione.
- Glutathione - Mentioned as a compound that is poorly bioavailable orally.
- Nitric Oxide - Mentioned as an example of a product with potentially poor efficacy due to bioavailability issues.
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) - Mentioned as a standard that dietary supplements generally do not adhere to, unlike pharmaceuticals.
- Food Grade - Mentioned as the standard required for selling dietary supplements.
- NSF Certification - Mentioned as a trustworthy label, especially for professional athletes.
- COA (Certificate of Analysis) - Mentioned as a document showing quality assurance, which consumers should look for.
- Trust Alliance - Mentioned as an initiative by TrueNigen to create an alliance for trustworthy supplement companies.
- Dairy - Discussed for its NR content and healing potential.
- Sirtuins - Mentioned as genes believed to be activated by caloric restriction, with research initially focusing on resveratrol.
- Resveratrol - Mentioned as a molecule found in red grapes, initially thought to mimic caloric restriction and activate sirtuins, but research suggests otherwise.
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) - Discussed in relation to its potential impact on longevity, consciousness uploading, and personalized health insights.
- Rapamycin - Mentioned as a molecule discussed for anti-aging potential, though the speaker is skeptical of its life-prolonging effects.
- Metformin - Mentioned as a molecule discussed for anti-aging potential, though the speaker is skeptical of its life-prolonging effects.
- Fatigue - Mentioned as a primary symptom of conditions like Lyme disease, mononucleosis, and long COVID, potentially benefiting from NAD elevation.
- Brain Fog - Mentioned as a symptom of long COVID.
- Sleep Issues - Mentioned as a symptom of long COVID.
- Long COVID - Discussed as a disease with predominant symptoms of fatigue, brain fog, depression, and sleep issues, with a study on NR showing dramatic differences after extended treatment.
- Vitamin D - Discussed as a critical nutrient, with many people being low in it, and ongoing drug development related to it.
- Zinc - Mentioned as an ingredient in TrueNigen's "TrueNigen Immune" product.
- Vitamin C - Mentioned as an ingredient in TrueNigen's "TrueNigen Immune" product.
- Creatine - Mentioned as an ingredient gaining popularity, with skepticism regarding its longevity benefits until more independent data is available.
- Magnesium - Mentioned as an example of a mineral where blood tests are not very valuable due to storage in bones and tissues.
- Plasma - Mentioned as a component of blood where NAD levels can be measured, but not necessarily indicative of tissue levels.
- Red Blood Cells - Mentioned as a place where NAD needs to be present to make its way into tissues.
- Blood Brain Barrier - Mentioned as a barrier that NAD must cross to reach the brain.
- Circadian Rhythms - Mentioned as being tied to NAD levels, impacting energy metabolism during time zone changes.
- Allostatic Load - Mentioned as the cumulative stress on the body, which can affect NAD levels.
- Niacin Flush - Discussed as a side effect of