Exoplanet Habitability, Pandemic Roots, and Ant Survival Strategies
TL;DR
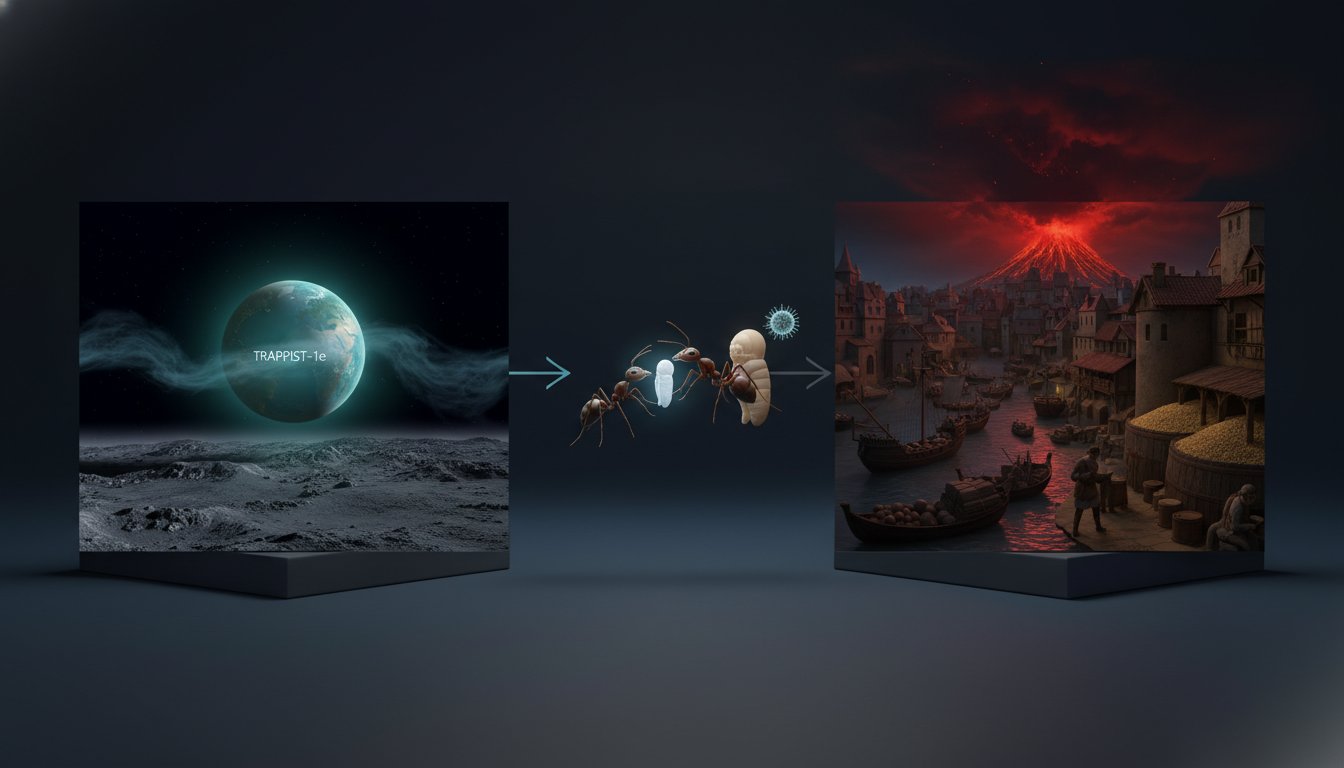
- Exoplanet TRAPPIST-1e, despite being Earth-sized and in the habitable zone, likely lacks the CO2 and methane necessary for life, suggesting habitable exoplanets may be rarer than anticipated.
- The Black Death pandemic's spread may have been exacerbated by volcanic activity in 1345 causing climate downturns, crop failures, and subsequent grain imports that facilitated rodent-borne bacteria transmission.
- Sick ants self-sacrifice by emitting chemical signals that prompt nestmates to destroy them, preventing the spread of infections like fungus and protecting the colony's survival.
- Future queen pupae, unlike worker ants, do not signal for destruction when infected and possess the ability to fight off infections independently, ensuring colony leadership continuity.
Deep Dive
New findings on exoplanets and ancient pandemics challenge prior assumptions, suggesting that the search for extraterrestrial life may require a recalibration of expectations and that historical disease outbreaks could have deeper climatic roots than previously understood. These developments highlight the dynamic nature of scientific discovery, where initial optimism can be tempered by complex data, and where seemingly unrelated phenomena, like volcanic activity and pandemics, can be causally linked.
Astronomers have discovered over 6,000 exoplanets, with TRAPPIST-1e initially appearing as a prime candidate for hosting life. This Earth-sized, rocky planet orbits its star within the habitable "Goldilocks Zone," where conditions could allow for liquid water. The presence of an atmosphere is considered crucial for habitability, as it regulates temperature and facilitates liquid water. However, recent in-depth studies of TRAPPIST-1e, published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, have revealed a significant setback: the exoplanet likely lacks an atmosphere, with no detected CO2 or methane, key potential biosignatures. This finding suggests that "exotitans" -- titan-like exoplanets with atmospheres -- may be rarer than anticipated, potentially indicating a lower prevalence of habitable exoplanets than previously hoped. The implication is that scientists may need to refine their search criteria and rely on more advanced observational tools to identify truly promising candidates.
Shifting to Earth's history, new research proposes a compelling link between volcanic activity and the Black Death pandemic, which devastated Europe in the mid-14th century. While the bacterium Yersinia pestis, spread by fleas on rodents, is the known pathogen, the reason for such a widespread rodent infestation prior to the plague's arrival in Italy in 1347 has been debated. A hypothesis suggests that volcanic eruptions around 1345 led to global sulfate aerosol dispersal in the atmosphere. This atmospheric change, according to researchers who examined ancient tree rings and ice cores, likely caused extreme rainfall, widespread flooding, and subsequent crop failures across Europe. This climate downturn, in turn, may have driven increased grain trade from the Mongol Empire to Genoa, inadvertently facilitating the transport of infected rodents. Thus, a major pandemic could have been indirectly triggered by climate disruption, underscoring how environmental shifts can have profound and cascading impacts on human health and history.
Finally, research into ant behavior reveals a stark mechanism for colony survival: sick ants signal for their own destruction. Studies published in Nature Communications show that infected ant pupae emit chemical signals that alert worker ants to their compromised state. Worker ants then respond by destroying the infected pupae and disinfecting the area with formic acid, thereby preventing the spread of contagion to the rest of the colony. This self-sacrifice is a critical survival trait for the colony as a whole. Notably, future queen pupae, even when infected, do not emit this signal and can often fight off infections independently. This distinction highlights a built-in hierarchy, where the survival of the individual future queen is prioritized over the immediate colony's risk, contrasting with the self-sacrificing behavior of worker pupae.
The overarching implication of these findings is that our understanding of both the universe and our planet's past is continuously evolving. The TRAPPIST-1e results temper expectations for finding life elsewhere, emphasizing the need for more sophisticated detection methods. The Black Death hypothesis, meanwhile, deepens our appreciation for how climate and environmental factors can act as significant, albeit indirect, drivers of historical pandemics. The ant study showcases a complex biological strategy for survival, demonstrating that even seemingly simple organisms employ sophisticated mechanisms to ensure the continuation of their species.
Action Items
- Audit exoplanet habitability criteria: Focus on atmospheric composition (CO2, methane) and liquid water potential for 3-5 candidate planets.
- Analyze climate impact on pandemics: Investigate historical volcanic activity and its correlation with crop failure and disease spread for 2-3 major historical events.
- Design ant colony defense protocol: Develop a system to identify and isolate infected pupae based on chemical signaling, prioritizing queen pupae.
- Measure exoplanet atmosphere detection limits: Determine the minimum atmospheric molecule concentration detectable with current telescopes for 5-10 exoplanets.
Key Quotes
"The reason this zone is important is because it's not too hot such that water evaporates off the surface and not too cold such that the planet would be covered in ice."
Regina Barber explains that the "Goldilocks Zone" is crucial for habitability because it maintains temperatures suitable for liquid water. This temperature range prevents water from boiling away or freezing solid, creating conditions where life as we know it could potentially exist.
"Now what the study is saying is that we have the best chances of finding life there in the goldilocks zone as opposed to some of these other exoplanet systems."
Regina Barber highlights that the study suggests exoplanet TRAPPIST-1e, located within its star's habitable zone, offers the most promising prospects for detecting extraterrestrial life. This positioning makes it a prime target for further scientific investigation compared to other discovered exoplanets.
"So when trappist 1e orbits its star it occasionally passes between the star and us viewing it sort of eclipsing the star so when that happens the starlight goes through the exoplanet's atmosphere if it has one and studying that light can show if the atmosphere has certain molecules like co2 or methane and co2 and methane could be but don't have to be signs of life."
Regina Barber describes a method for analyzing exoplanet atmospheres, explaining that when TRAPPIST-1e passes in front of its star, the starlight filters through its atmosphere. Studying this filtered light can reveal the presence of molecules like carbon dioxide or methane, which could potentially indicate life.
"His team hypothesized that volcanic activity in 1345 led to extreme rainfall it also led to widespread flooding and ultimately crop failure throughout europe."
Regina Barber relays a hypothesis suggesting that volcanic eruptions in 1345 may have triggered a climate downturn. This downturn, according to the hypothesis, resulted in excessive rainfall, extensive flooding, and subsequent crop failures across Europe.
"So a study in the journal nature communications found that sick ants send chemical messages to their nestmates signaling that they're sick then worker ants pick up those signals and destroy the sick ants before they infect the others because you know like a fungal infection could take out the whole colony."
Regina Barber explains a study's findings on ant behavior, where sick ants emit chemical signals to alert their colony mates. This communication prompts worker ants to eliminate the infected individuals, thereby preventing the spread of diseases like fungal infections that could devastate the entire colony.
"First the worker ants peel off the cocoon and then they bite holes in the pupae and then they spray in formic acid and this basically serves to disinfect the infected pupa because it kills off the fungus and while the acid kills off the fungus it also kills the pupae."
Regina Barber details the process of how worker ants eliminate infected pupae, describing how they remove the cocoon, puncture the pupa, and then apply formic acid. This acid serves a dual purpose: it eradicates the fungal infection and, in the process, kills the pupa itself.
Resources
External Resources
Books
- "Astrophysical Journal Letters" - Mentioned as the publication venue for a recent study about exoplanet TRAPPIST-1e.
Research & Studies
- Study on TRAPPIST-1e (Institution not specified) - Discussed for its findings that the exoplanet may lack an atmosphere and methane, suggesting it might not be as habitable as previously thought.
- Study on Black Death causation (Arizona State University, Germany) - Referenced for the hypothesis that volcanic activity in 1345 led to climate downturn, crop failure, and ultimately the spread of the Black Death.
- Study on sick ants (Nature Communications) - Discussed for revealing that sick ants signal nestmates to destroy them to prevent colony-wide infection.
People
- Hannah Barker - Historian at Arizona State University, mentioned for discovering the reopening of the grain trade between the Mongol Empire and Genoa in 1347.
- Martin Blach - Historian in Germany, mentioned for hypothesizing that volcanic eruptions prior to the Black Death led to climate downturn and crop failure.
- Ulf Buntkin - Colleague of Martin Blach, mentioned for his work on ancient tree ring samples and ice cores related to volcanic activity.
- Erica Dawson - Study author, mentioned for explaining the process by which sick ants signal for their own destruction.
Organizations & Institutions
- NPR - Mentioned as a public media organization that relies on listener support and produces the podcast "Short Wave."
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) - Mentioned in relation to clinical trials for cancer breakthroughs.
- AT&T - Mentioned as a telecommunications company with a fast and reliable network.
- Dell Technologies - Mentioned as a provider of PCs with Intel Core Ultra processors.
- Edward Jones - Mentioned as a financial advisory firm with over 100 years of experience.
- Solidigm - Mentioned as a provider of solid-state storage solutions optimized for AI.
- Rosetta Stone - Mentioned as an expert in language learning.
- Donors Choose - Mentioned as an organization that connects public school teachers with donors for classroom needs.
Podcasts & Audio
- Short Wave (NPR) - The podcast hosting the episode, discussed for its science reporting and listener support model.
- Consider This (NPR) - Mentioned as a podcast where Elsa Chang can be heard.
Other Resources
- Goldilocks Zone - Referenced as the habitable zone around a star where a planet can maintain liquid water.
- Exotitans - Mentioned as a category of titan-like exoplanets that most likely lack an atmosphere.
- Black Death - Referenced as a major pandemic in human history that occurred in the Middle Ages.
- Public Media - Discussed as a concept that relies on listener support and aims to deliver understanding of the world.