AI's Early Impact, Shifting Economy, and Market Consolidation
TL;DR
- AI adoption is in its early stages, with the focus currently on infrastructure, and is projected to contribute only a half-percentage point gain in productivity growth to GDP over the next five years.
- The Federal Reserve is operating at or near a neutral interest rate, requiring a change in economic conditions like worsening unemployment or improved inflation to justify rate adjustments.
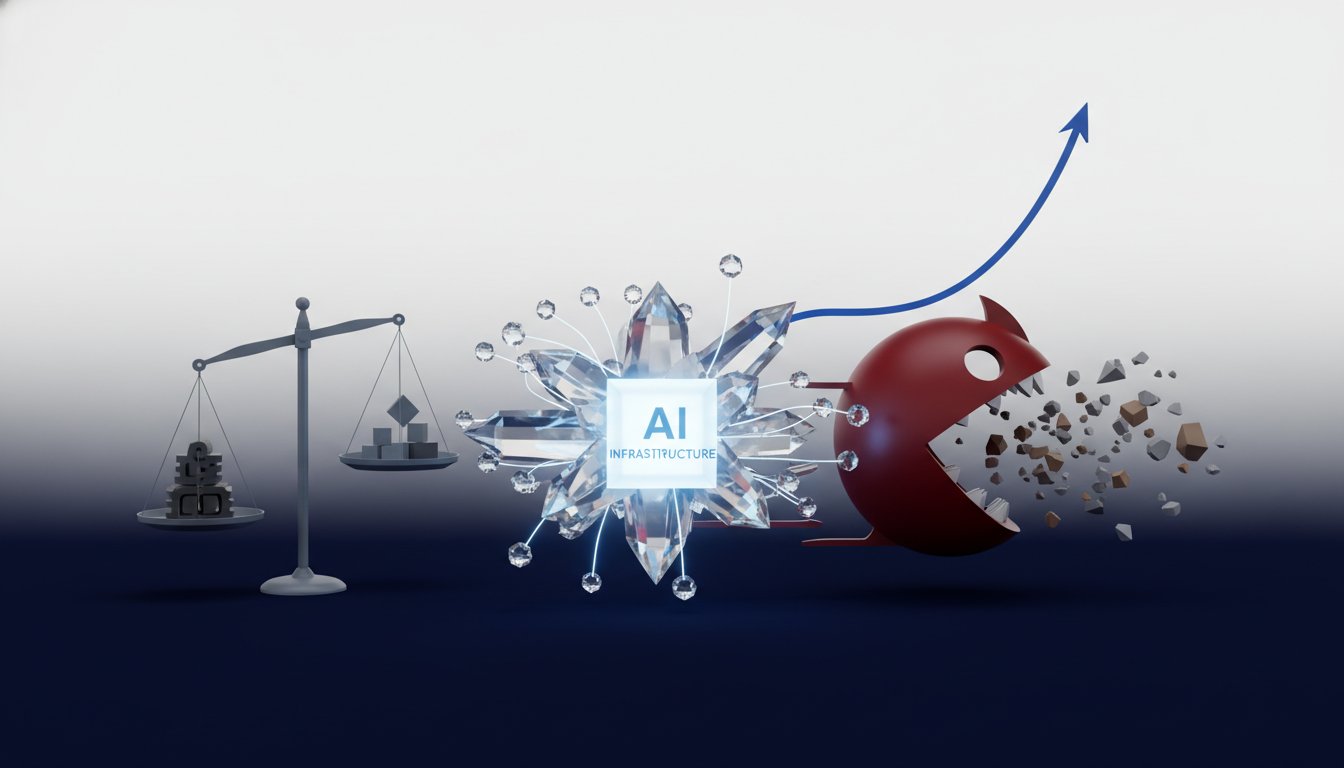
- The US economy is shifting from a "K-shaped" recovery to a "Pac-Man" pattern, where the top income distribution continues to appreciate while the bottom 50th percentile's economic fortunes have flatlined.
- Merger and acquisition activity is driven by a need for size and scale to afford technology investments, leading to a potential consolidation trend in American capitalism.
- Private credit has become a valuable addition to bank lending, but caution is advised for less investment-grade private credit due to the potential for an eventual credit cycle.
- Global yield curves are steepening due to increased government debt issuance and the fading of central banks as indiscriminate buyers, demanding higher yields from the private sector.
- The UK bond market presents a significant opportunity due to sticky inflation pressures and the Bank of England's potential for more easing, offering value amidst perceived chaos.
- The emergence of new job titles, such as knowledge architects and conversation designers, is directly linked to the increasing prevalence of AI models in industry.
Deep Dive
The U.S. economy is navigating a complex landscape, balancing the potential productivity gains from AI against persistent economic headwinds and a shifting consumer landscape. While AI promises significant, albeit long-term, economic uplift, its immediate impact is less clear, with much of the current investment focused on infrastructure rather than widespread adoption. Simultaneously, the economy is grappling with the dual mandate of the Federal Reserve, which faces the challenge of managing both inflation and employment in a post-pandemic environment marked by government spending and supply chain disruptions.
This dynamic creates a bifurcated economic reality, characterized by a "Pac-Man" pattern where the top earners and wealth holders continue to prosper, while the bottom half of the income distribution experiences flatlined economic fortunes, despite some positive indicators like increased net worth and a declining Gini coefficient in recent years. This fragility in the lower-income segments, coupled with a tepid housing market and volatile oil prices, means that broad-based economic gains are not guaranteed. Policymakers face the critical task of seeding investments that enhance productivity and quality of life for all citizens, particularly in areas like affordable housing, to ensure a more inclusive economic future.
The ongoing merger and acquisition activity, driven by the need for scale to afford technological investments, suggests a trend towards consolidation in many industries. However, this is occurring alongside the emergence of smaller, AI-powered businesses. This indicates a future market structure that will likely include dominant large companies, numerous small emerging businesses, and a substantial middle ground, where companies must strategically invest in efficiency and technology to remain competitive. In the fixed income markets, while credit spreads are tight, corporate fundamentals appear healthy, and the global steepening of yield curves, driven by increased government debt issuance and the fading role of central banks as indiscriminate buyers, presents attractive opportunities for investors seeking both income and diversification. However, caution is advised regarding the less investment-grade segments of private credit, given the lack of recent credit cycles.
Action Items
- Audit AI adoption: Assess 3-5 core business processes for incremental spending versus shifting IT budgets to understand true AI impact.
- Measure "Pac-Man" economy effect: For 3-5 income segments, track net worth and real income changes to validate the "Pac-Man" economic pattern.
- Analyze UK fixed income value: Evaluate 3-5 UK bond market opportunities, considering sticky inflation and potential Bank of England easing bias.
- Track AI-driven job creation: Identify 5-10 emerging job titles related to AI to understand evolving skill demands and workforce shifts.
Key Quotes
"well i think we're in the early stages of ai adoption most of the talk about ai right now is about the infrastructure build but that's different than the downstream adoption we're in the first or second inning uh i think my own view and i think the view of my firm is when we talk five years from now we'll see a half a percentage point gain in productivity growth for gdp uh and it will help business but which use cases work and which don't we're going to spend the next three years uh trying to figure that out"
Robert Kaplan explains that while the infrastructure for AI is being built, its widespread adoption and impact on productivity are still in their early stages. Kaplan anticipates a modest productivity gain of about half a percentage point in GDP over the next five years, but acknowledges that identifying successful use cases will require further exploration over the next three years.
"i think the neutral rate nominal is about three and a half three and three quarters and some of the folks say with inflation at two and three quarters and the job market likely to firm in the next year we shouldn't be at neutral and i think overall they bought insurance in case the labor markets weaker than they thought but from here it will be a conventional fed meaning something's got to change to move the rate either unemployment needs to worsen or inflation needs to improve across the nation"
Robert Kaplan discusses the Federal Reserve's policy stance, noting that while the neutral interest rate is estimated to be around 3.5% to 3.75%, some believe the current rate is too high given inflation and the expected strengthening of the job market. Kaplan suggests the Fed may have increased rates as a precautionary measure against potential labor market weakness, and future rate adjustments will depend on changes in unemployment or inflation.
"well for a lot of the last 10 or 15 years uh the fed had the luxury pre covid of not having an inflation problem so it could focus heavily on what was going on in employment and if thought employment was weakening it could move uh post covid and i would argue with this boom in government spending we had in 2021 2022 and 2023 and that which probably caused supply chain dynamics to create an excess demand issue uh they got to deal with both and it's harder to deal with both and so then they have to make trade off decisions and that's hard to do"
Robert Kaplan explains the Federal Reserve's challenge in managing both inflation and employment post-COVID, a situation more complex than the pre-pandemic era. Kaplan notes that before COVID, the Fed could prioritize employment due to low inflation, but the significant government spending and resulting supply chain issues have created excess demand, forcing the Fed to balance both mandates, which he describes as a difficult trade-off.
"it's 100 a us focused game this is very exclusively if you're in capital markets and you're in ai it's us if you're in government spending it's china and europe is still sort of looking askance at the whole thing so i think there's a fomo element here as well with companies and they need to communicate to their shareholders that they're investing in next generation technology which today is ai"
Alexis Crow highlights that the current AI investment landscape is primarily US-centric, particularly in capital markets, while government spending in this area is concentrated in China. Crow suggests that companies are investing in AI to demonstrate to shareholders that they are adopting next-generation technology, driven partly by a "fear of missing out" (FOMO).
"i mean i think one thing that's striking tom is that over time the availability of key skills has been a key pressure point and a key concern for ceos regardless of jurisdiction regardless of sector and so i think ai is meant to be this panacea that's going to solve the world of all of its ills if we're thinking about a shortage of skills if we're thinking about an uplift in productivity if we're thinking about investment to support capital markets and returns and consumer firepower and so that continues to be the buzzword"
Alexis Crow points out that the availability of key skills has consistently been a major concern for CEOs across all sectors and regions. Crow notes that AI is often presented as a solution to various issues, including skill shortages, productivity improvements, and support for capital markets, making it a prominent topic of discussion.
"exclusively in the united states we have a situation where the k the top part of the k continues to appreciate right the top parts of the income distribution spending income wealth purchasing power all appreciating significantly but rather than a k the bottom part of the income distribution the bottom 50th percentile has flatlined it's not continuing to tumble okay net worth held by the bottom 50th percentile in the united states has more than doubled over the last five years 4 2 trillion really i didn't know okay we had a gini coefficient which is you know technical technical way of looking at inequality actually tumbled by the single greatest amount on record 2019 to 2021"
Alexis Crow describes the US economy as a "Pac-Man" pattern, where the top income earners are experiencing significant gains in spending, income, wealth, and purchasing power. Crow contrasts this with the bottom 50th percentile, whose economic fortunes have flatlined, though she notes that the net worth of this group has doubled in the last five years and the Gini coefficient, a measure of inequality, has significantly decreased.
"i think it's going to be a similar environment and i think what we heard we heard obviously from powell yesterday um they still got that easing bias in i think whatever the kind of really interesting comments that he's kind of almost slammed the door shut no one was really predicting hikes as the next the next move that said obviously yields have come down a long way so it's really in my mind more of a carry environment but that's still reasonably attractive carry and then you get the uh the opportunity that if things do go wrong you know the diversification of bonds i think is back which means there's a lot of capital gains if this labor market continues to deteriorate further and faster than the market expects and probably we expect"
Iain Stealey anticipates a similar market environment for the upcoming year, influenced by the Federal Reserve's easing bias. Stealey notes that while no one expected further rate hikes, yields have decreased significantly, leading to a "carry environment" that remains attractive. He also highlights the return of bond diversification as a source of potential capital gains if the labor market deteriorates more than expected.
"i think i think you make a good point there because it's the viewers should be aware that this isn't just a us phenomenon that curves are steepening around japan around the world japan outrageously but even if you look at the uk if you look at germany and the eurozone curves are steepening and that's partly because we're getting closer to the end of the the easing cycle again let's see what happens with the data on that but also there's a huge amount of government debt being issued globally
Resources
External Resources
Books
- "The Great Gatsby" by F. Scott Fitzgerald - Mentioned in relation to the concept of a "gilded age" and societal inequality.
Articles & Papers
- LinkedIn research regarding jobs that didn't exist 25 years ago (Wall Street Journal) - Discussed as an example of evolving job titles due to technological advancements, particularly AI.
People
- Robert Kaplan - Vice Chairman at Goldman Sachs, former President of the Dallas Fed, discussed Federal Reserve policy and economic outlook.
- Alexis Crow - Partner & Chief Economist at PwC US, discussed the American economy's shift to a "Pac-Man" pattern and CEO concerns about skills availability.
- Iain Stealey - International CIO for Fixed Income at JPMorgan Asset Management, discussed fixed income markets, particularly in the UK, and opportunities in bond markets.
- Austin Goolsby - Mentioned for his dissent at the Fed meeting and his work out of MIT and Chicago, noted as someone to watch.
- Mark Wynn - Mentioned for a spectacular essay on AI, with his work summarized as "we just don't know."
- Hugh van Steen - Mentioned as being over at Oliver Wyman, having worked extensively in the field.
- Patrick Gambel - Mentioned in the context of old industry and building size and scale.
- Mr. Diamond - Mentioned in relation to a building program in Canary Wharf.
- Mr. Griffith - Mentioned in relation to the Citadel palace in Miami Beach.
- Bob Michael - Mentioned as someone to bring to the show next time.
Organizations & Institutions
- Goldman Sachs - Mentioned as the firm Robert Kaplan is with.
- PwC US (PricewaterhouseCoopers) - Mentioned as the firm Alexis Crow is a partner and chief economist at.
- JPMorgan Asset Management - Mentioned for its active fixed income ETFs and global leadership in the business.
- Federal Reserve - Discussed in relation to its policy path, rate cuts, and the dual mandate.
- Dallas Fed - Mentioned in relation to Robert Kaplan's former public service.
- MIT - Mentioned as a place Austin Goolsby's work is out of.
- University of Chicago - Mentioned as a place Austin Goolsby's work is out of.
- Rochester - Mentioned in relation to Mark Wynn.
- Oliver Wyman - Mentioned as a firm where Hugh van Steen works.
- St. Andrews - Mentioned in relation to Alexis Crow's education and a cafe.
- London School of Economics (LSE) - Mentioned in relation to Alexis Crow's education.
- Ernst & Young - Mentioned as one of the major accounting firms.
- Deloitte - Mentioned as one of the major accounting firms.
- Warner Brothers Discovery - Mentioned in relation to a large M&A trade.
- Morgan Stanley - Mentioned in relation to Skelly and Deck.
- Citadel - Mentioned in relation to a palace in Miami Beach.
- Watches of Switzerland - Mentioned as being in Canary Wharf.
- CFA Society Phoenix - Mentioned as an event in March at the Omni Scottsdale Montelucia.
- Tottenham - Mentioned in relation to Son, a player.
Tools & Software
- Adobe Acrobat Studio - Mentioned for its AI-powered PDF spaces and capabilities.
- Bloomberg Terminal - Mentioned in relation to looking at fixed income returns.
Websites & Online Resources
- jpmorgan.com/getactive - Mentioned for learning more about J.P. Morgan Asset Management's active fixed income ETFs.
- mastercard.com/commercialacceptance - Mentioned for discovering Mastercard's solutions for B2B acceptance.
- adobe.com/dothatwithacrobat - Mentioned for learning more about Adobe Acrobat Studio.
- chase.com/businesscard - Mentioned for learning more about Chase for Business credit cards.
- public.com/market - Mentioned for transferring a portfolio and earning a bonus.
- public.com/disclosures - Mentioned for complete disclosures regarding generated assets.
Other Resources
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) - Discussed as a driver of productivity growth, new job titles, and merger activity.
- K-shaped economy - Mentioned as a pattern of economic distribution.
- Pac-Man economy - Presented as an alternative view to the K-shaped economy, describing shifts in the American economy.
- Gini coefficient - Mentioned as a technical way of looking at inequality.
- Dual mandate - Discussed in relation to the Federal Reserve's focus on inflation and employment.
- Neutral rate - Discussed in the context of Federal Reserve policy.
- Private credit - Discussed as an addition to bank lending, with a caution on the less investment grade side.
- Generated assets - Mentioned as a feature on Public, allowing users to turn ideas into investable indexes with AI.
- All-inclusive adventure resorts - Discussed as a growing trend in the travel industry.
- Pay TV customers - Mentioned in the context of fierce competition and YouTube's customization strategies.
- Repatha (evolocumab) - Mentioned as a medication that lowers LDL cholesterol and heart attack risk when used with a statin.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) - Discussed in relation to health disparities and diagnosis challenges.
- Wayfinder (podcast) - Mentioned as a special episode brought to you by Virgin Voyages.
- Health Discovered (podcast) - Mentioned as a podcast that takes a closer look at MS.