Accelerated Computing Powers AI's Essential Infrastructure and Job Evolution
TL;DR
- The shift to accelerated computing, driven by the end of Moore's Law, makes NVIDIA's infrastructure essential for AI development, irrespective of AI bubble narratives.
- AI's impact on jobs is nuanced; while tasks may be automated, the purpose of roles evolves, creating new demands for skilled labor in infrastructure and specialized fields.
- Open-source AI is crucial for fostering innovation across industries, enabling startups and established companies to adapt and build specialized applications without being stifled.
- The AI industry's rapid progress in reasoning and grounding is mitigating skepticism around hallucination, making AI a trusted tool for experts in fields like medicine and law.
- The declining cost of AI compute and token generation, driven by hardware and algorithmic advancements, democratizes access and fuels new application development across diverse sectors.
- Robotics, empowered by advancements in generative AI, multimodal capabilities, and reasoning systems, is poised to address severe labor shortages and create new industries.
- The future of AI development hinges on a diverse, multi-layered approach, emphasizing programmable architectures and open-source contributions to maintain technological leadership and drive innovation.
Deep Dive
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang argues that the fundamental shift from general-purpose to accelerated computing, driven by the end of Moore's Law, is the primary engine of technological advancement, with AI being a critical, but not singular, beneficiary. This profound change is not a bubble but a necessary evolution of computing, creating immense demand for infrastructure and fostering new industries. The narrative that AI will cause widespread job loss is a misunderstanding of how technology augments, rather than replaces, human purpose, and that AI's true value lies in its ability to solve previously intractable problems and address labor shortages.
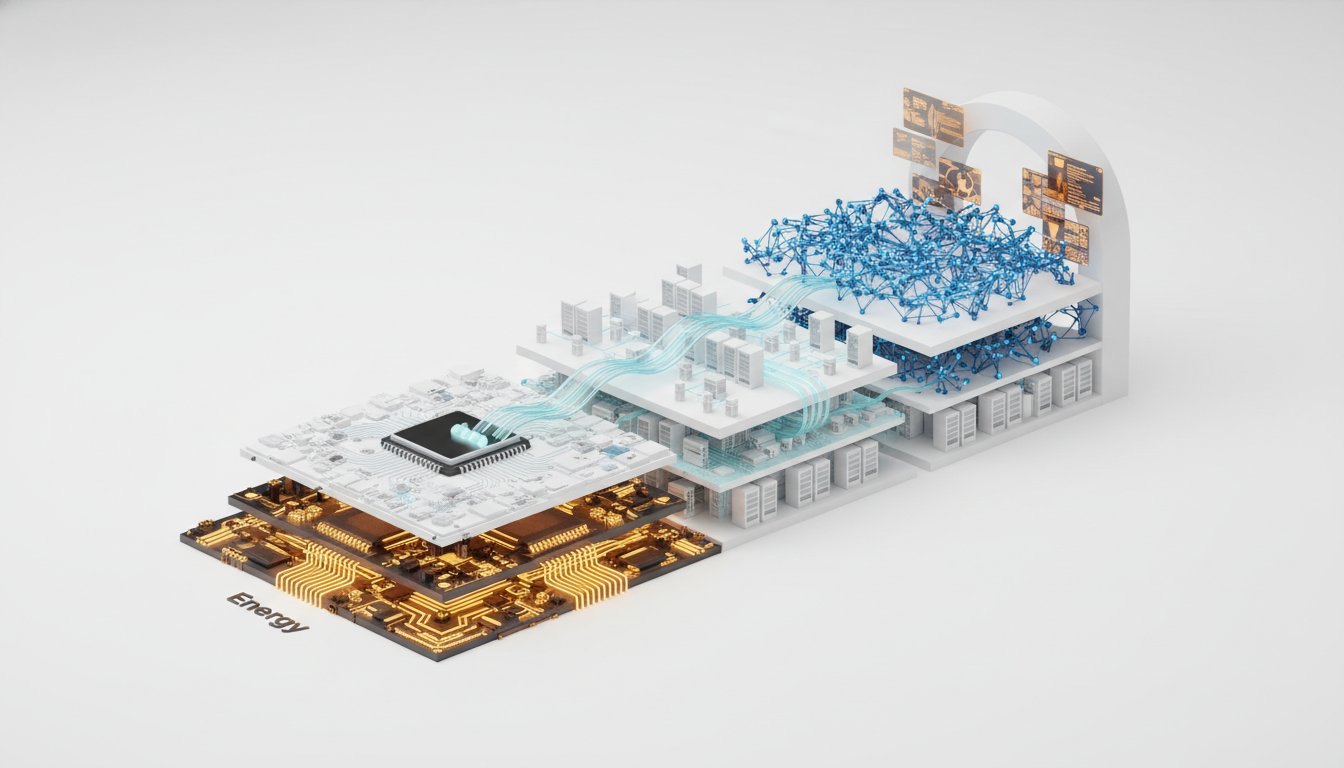
The AI revolution is characterized by a multi-layered technological stack, from energy and chips to infrastructure, models, and applications. Within this stack, open source plays a crucial role in democratizing access and fostering innovation across diverse industries, countering the notion that a single monolithic player or model will dominate. Huang emphasizes that the rapid decrease in AI compute costs, driven by hardware and algorithmic advancements, enables widespread adoption and the emergence of specialized, high-value applications. This cost reduction, coupled with the growing demand for AI capabilities across scientific research, finance, autonomous systems, and digital biology, indicates sustained growth rather than a speculative bubble. The industry's focus is shifting from pure scaling to research and development, allowing for diversification and niche specialization. Huang projects that key sectors like digital biology and robotics will experience their "ChatGPT moment" as AI's reasoning capabilities mature and multimodal understanding becomes more robust, addressing critical labor shortages and enabling new forms of human-robot interaction. He advocates for a pragmatic approach to AI regulation, emphasizing that technological progress, rather than restrictive policies, is key to safety and societal benefit. Huang also expresses optimism for improved US-China relations, advocating for a nuanced strategy that recognizes interdependence while promoting independence.
The second-order implications are significant: the demand for accelerated computing infrastructure is projected to continue its exponential growth, driving investment in chip manufacturing, data centers, and energy production. This will fundamentally reshape global economies and employment landscapes, not by eliminating jobs, but by redefining them around human purpose and augmenting capabilities. The proliferation of specialized AI applications will create new markets and opportunities, particularly in fields like digital biology and advanced robotics, which promise to tackle complex global challenges. Furthermore, the emphasis on open source and a diverse technological stack suggests a future where innovation is distributed, with the US maintaining its competitive edge through leadership across the entire ecosystem, rather than relying on a single dominant entity. The narrative around AI's impact on jobs, particularly the doomsday scenarios, is challenged by the historical pattern of technological adoption, which shows augmentation and the creation of new roles focused on higher-level problem-solving and purpose-driven work. The energy sector will be intrinsically linked to AI's growth, with demand driving innovation in sustainable energy solutions. Finally, the ongoing advancements in AI reasoning and multimodality will accelerate breakthroughs in fields previously constrained by human capacity, from scientific discovery to complex physical tasks performed by robots.
Action Items
- Audit AI reasoning models: Evaluate 3-5 core models for hallucination and grounding accuracy using synthetic data generation (ref: Open Evidence).
- Create runbook template: Define 5 required sections (setup, common failures, rollback, monitoring) for AI infrastructure deployment to prevent knowledge silos.
- Implement mutation testing: Target 3 core AI modules to identify untested edge cases beyond coverage metrics for improved reliability.
- Track 5-10 high-variance AI events per deployment (e.g., unexpected reasoning failures, grounding errors) to measure outcome impact and inform future development.
- Measure AI performance disconnect: For 3-5 AI applications, calculate correlation between perceived usefulness and actual task completion metrics.
Key Quotes
"I think the whole industry addressed one of the biggest skeptical responses of AI, which is hallucination and generating gibberish. I thought that this year, the whole industry -- everything from every field, from language to vision to robotics to self-driving cars -- the application of reasoning and the grounding of the answers made big, big leaps."
Jensen Huang highlights that the AI industry has made significant progress in addressing the issue of hallucination, a common criticism where AI generates nonsensical or fabricated information. He notes that across various domains like language, vision, and robotics, the integration of reasoning capabilities and grounding of answers has led to substantial improvements in AI accuracy and reliability.
"The thing that's really quite unique about AI is that it needs these computers to generate these tokens every single time. I call them AI factories because it's producing tokens that will be used all over the world. Now, some people would say it's also part of infrastructure. The reason why it's infrastructure is because obviously it affects every single application, it's used in every single company, it's used in every single industry, it's used in every single country."
Jensen Huang explains that AI's reliance on continuous computation to generate output, which he terms "AI factories," positions it as fundamental infrastructure. He emphasizes that this infrastructure is pervasive, impacting every application, company, industry, and country globally due to its essential role in producing the tokens that power AI functionalities.
"The question is what is the purpose of the job versus what is the task that you do in your job? As you know, I spend most of my day typing. That's my task, but my purpose is obviously not typing. So the fact that somebody could use AI to automate a lot of my typing, and I really appreciate that, and it helps a lot."
Jensen Huang introduces a framework to understand the impact of AI on jobs by distinguishing between the "purpose" of a job and the "tasks" involved. He uses his own experience with typing as a task, while his purpose is broader, suggesting that AI can automate tasks, freeing individuals to focus on the higher-level purpose of their roles, thereby increasing overall productivity and value.
"Well, this five-layer stack is one way of thinking about it. And then the next way of thinking about it is AI's really diverse. When you now have this framework of what the technology capabilities are, how to build the technology, and how diverse it is, then you can come back and think about, okay, let's ask the question, how important is open source?"
Jensen Huang presents a five-layer framework for understanding the AI technology stack, from energy at the base to applications at the top. He then pivots to discuss the diversity of AI and uses this framework to contextualize the importance of open source, suggesting that its role is critical across various layers and applications within the broader AI ecosystem.
"The reason why we are so dedicated to a programmable architecture versus a fixed architecture. Remember a long time ago, a CNN chip came along and they said, NVIDIA done. And then a transformer chip came and NVIDIA was done. People are still trying that. Yes. And the benefit of these dedicated ASICs, of course, it could perform a job really, really well. And transformers is a much more universal AI network. But the transformer, as you know, the species of it is growing incredibly."
Jensen Huang explains NVIDIA's strategic focus on programmable architectures over fixed ones, referencing past predictions of their obsolescence due to new chip designs like CNNs and transformers. He highlights that while specialized ASICs excel at specific tasks, the adaptability of transformer architectures, which are rapidly evolving, necessitates a flexible, programmable approach to maintain technological leadership.
"I am optimistic that our relationship with China will improve, that President Trump and the administration has a really, really grounded and common sense attitude and philosophy around how to think about China. That they're an adversary, but they're also a partner in many ways, and that the idea of decoupling is naive."
Jensen Huang expresses optimism about improving US-China relations, attributing this to a pragmatic approach from the Trump administration that views China as both an adversary and a partner. He argues that the concept of complete decoupling is unrealistic, emphasizing the deep interdependence between the two nations and the need for a nuanced strategy to manage their relationship productively for global benefit.
Resources
External Resources
Books
- "The AI Revolution in Medicine: Beyond the Hype" by [Author Not Specified] - Mentioned as a resource for understanding the practical applications of AI in healthcare.
Articles & Papers
- "DeepSeek Coder" (DeepSeek AI) - Discussed as a significant open-source contribution that benefited American startups and AI labs.
People
- Jensen Huang - Guest, CEO of NVIDIA, discussing AI, robotics, and industry trends.
- Andre Karpathy - Mentioned for his estimations on the cost of building AI models and his views on the current age of AI research.
- Geoffrey Hinton - Referenced for his past prediction about AI revolutionizing radiology.
Organizations & Institutions
- NVIDIA - Primary subject of discussion regarding accelerated computing, AI hardware, and industry trends.
- OpenAI - Mentioned in relation to revenue and capacity needs for AI models.
- TSMC - Referenced as a company building more chip plants.
- SK Hynix - Mentioned as a company building more chip plants.
- Waymo - Discussed in the context of the evolution of self-driving car technology.
- Tesla - Mentioned in relation to self-driving car safety ratings and robotics.
- Stanford - Mentioned as the institution where Erin, the sister-in-law of a speaker, leads in nuclear medicine.
- Caterpillar - Referenced as an example of a vertical solution provider in industrial AI.
Websites & Online Resources
- OpenEvidence - Mentioned as a trusted resource for medical information and an example of an AI application.
- Harvey - Referenced as a trusted resource for legal information and an example of an AI application.
- Cursor - Discussed as a widely used AI coding tool benefiting software engineers.
- No Priors - Mentioned as the podcast where the discussion is taking place, with a call to action for subscriptions and email sign-ups.
Other Resources
- Scaling Laws - Mentioned as a concept that did not surprise the speaker, indicating predictable advancements in AI.
- Hallucination - Discussed as a major skeptical response to AI that the industry has addressed.
- Routers (in front of AI models) - Mentioned as a technology that enables AI models to perform necessary research based on confidence in answers.
- Token Generation Rate - Discussed as a metric for AI inference, particularly for reasoning tokens, and its rapid growth.
- Gross Margins - Referenced in the context of profitability for companies like OpenEvidence, Claude, and OpenAI.
- Mechatronics Technology - Mentioned as a technology that can be combined with AI to embody and perform tasks.
- Five Layer Cake (AI Technology Stack) - A framework used to explain the components of AI: Energy, Chips, Infrastructure, AI Models, and Applications.
- Open Source - Discussed extensively for its importance to startups, industries, and overall AI innovation.
- God AI - A concept discussed as an unhelpful and extreme future state of AI.
- Digital Biology - Identified as an industry poised for a "ChatGPT moment" with advancements in protein understanding, generation, and chemical understanding.
- Multi Protein Understanding, Representation Learning, and Generation - Mentioned in relation to the model "Lot Protina."
- Protein Folding and Protein Binding - Specific aspects of digital biology discussed.
- Molecule Design - Mentioned as an area where companies are working on end-to-end solutions.
- Chemical Understanding and Generation - Discussed in the context of digital biology advancements.
- World Foundation Model - A concept for a foundational model for proteins or cells.
- Human Robots / Multi Embodiment Robots - Discussed as a future area of breakthrough enabled by generative AI, multimodal models, and reasoning systems.
- Self-Driving Cars (Four Eras) - A framework used to explain the technological progression of autonomous vehicles.
- Programmable Architecture - Discussed as a key design principle for AI hardware that enables flexibility and adaptation.
- Moore's Law - Referenced as a historical trend in transistor advancement, contrasted with current AI hardware progress.
- MVLinks 72 - Mentioned as NVIDIA's latest innovation for low-cost token generation.
- Multi-modality - Identified as a key enabler for advanced chatbots and other AI applications.
- Long Context - Discussed as a factor enabling more sophisticated chatbots.
- Synthetic Data Generation - Highlighted as important for making AI models more grounded, diverse, and safe.
- Cybersecurity (using AI) - Mentioned as an area where AI is being applied.
- Lot Protina - An open model for multi-protein understanding, representation learning, and generation.
- Protein Generation - Identified as an area that will advance quickly.
- Chemical Understanding and Generation - Discussed in the context of digital biology.
- Reasoning Cars - A concept for autonomous vehicles that can think and navigate novel circumstances.
- Out of Domain / Out of Distribution (AI) - Addressed by reasoning systems.
- Pick and Place Robot - An example of a robotic application.
- Caterpillar - Mentioned as an example of a vertical solution provider.
- Cognition - Mentioned as a company benefiting from AI cost reductions.
- Great Firewall of China - Referenced in the context of China's internet policies and market access.
- Accelerated Computing - Discussed as a shift away from general-purpose computing due to Moore's Law limitations.
- Classical Machine Learning - Mentioned as a precursor to AI in areas like recommender systems and feature engineering.
- XGBoost - An example of classical machine learning.
- Recommender Systems - Mentioned as an application of classical machine learning.
- Feature Engineering - Discussed in the context of classical machine learning.
- Data Science Machine Learning Lifecycle - The overall process where accelerated computing is used.
- Chatbots (OpenAI, Tropick, Gemini) - Examples of AI models discussed in relation to revenue and capacity.
- NVIDIA's AV Business - Mentioned as a significant and growing segment.
- Robotaxis - Discussed as an application of AI and accelerated computing.
- Digital Biology (AI Work) - Mentioned as a fast-growing segment for NVIDIA.
- Quantitative Trading (Quants) - Discussed as a financial services application moving towards AI.
- Drug Discovery - Mentioned as an area undergoing a shift towards supercomputers and AI.
- R&D (Research and Development) - Discussed in the context of its scale and how it is being powered by AI infrastructure.
- MIT Study (Enterprise AI Deployments) - Referenced as a study claiming limited usefulness of enterprise AI deployments.
- Enterprise Sales (Harvey, CR, etc.) - Mentioned in the context of AI business progress.
- End-User Adopted AI - Discussed as a fast-growing category, even in conservative industries.
- Grounded Research - Highlighted as a key benefit of AI tools like OpenEvidence.
- Biomedical Knowledge - Discussed as a vast and accelerating area where AI assists professionals.
- Archive Papers - Mentioned as a task now handled by AI tools like ChatGPT.
- Search - Discussed as a task that is being replaced by AI for answers.
- Multi Layer Cake Framework - A recurring theme for understanding AI's diversity.
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) - Mentioned as an example of safety technology in cars.
- Lane Keeping - Mentioned as a safety feature in cars.
- FSD (Full Self-Driving) - Discussed as a positive advancement in automotive technology.
- Export Control Policy - Discussed in relation to national security and technology leadership.
- Huawei - Mentioned in the context of China's domestic chip capabilities.
- The Internet - Used as an analogy for understanding technology stacks and industry growth.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit) - Contrasted with accelerated computing.
- DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) - Mentioned in relation to capacity needs.
- Intel - Mentioned as a company benefiting from China's internet growth.
- AMD - Mentioned as a company benefiting from China's internet growth.
- Micron - Mentioned as a company benefiting from China's internet growth.
- Google - Mentioned as a company that may not have benefited from China's internet growth.
- Uber - Mentioned as a company that may not have benefited from China's internet growth.
- Great Firewall - Referenced in the context of China's internet policies.
- The Circular System (Economy, Military, Wealth) - A framework for understanding the interconnectedness of economic and military strength.
- The Stack (Technology Layers) - A concept used to analyze technology industries.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) - Not explicitly mentioned but implied in discussions of pervasive technology.
- AI Bubble - A narrative discussed and analyzed.
- NVIDIA's AV Business - Mentioned as a significant revenue driver.
- Supercomputers - Discussed as essential infrastructure for AI development.
- Multi-Company, Multi-Industry Shortage (Computing Capacity) - A key observation about current demand.
- Transformer Architecture - Discussed as a foundational AI network architecture.
- Attention Mechanism - A component of transformer architectures.
- Diffusion vs. Auto-Regressive Models - Different types of AI generation models.
- Hybrid SM Transformer - A type of transformer architecture.
- Nimotran - Mentioned as announcing a new hybrid SM transformer.
- Flash Attention - An algorithm that runs on NVIDIA hardware.
- CNNs (Convolutional Neural Networks) - Mentioned as still running everywhere.
- LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory) - Mentioned as still running everywhere.
- MoE (Mixture of Experts) - Discussed as a difficult but important architecture for inference.
- The Age of Research vs. The Age of Scaling - A distinction made about current AI development.
- Niche Leap - The idea that AI models can differentiate in specific segments.
- Boiling the Ocean - A metaphor for trying to do everything at once, contrasted with niche specialization.
- Pre-training - Discussed as a preparatory stage for AI model training.
- Post-training - A term used to describe the current phase of AI training.
- Compute Scaling - The direct translation of computational power to intelligence.
- Algorithmic Layer - One of the components driving AI cost reduction.
- Model Layer - Another component driving AI cost reduction.
- Tokenomics - The economics of token generation in AI.
- DeepSeek - Mentioned as a significant paper that influenced Silicon Valley researchers.
- Chinese Models - Discussed in the context of open-source AI contributions.
- US Models - Discussed in the context of closed-source AI development.
- American Startups - Beneficiaries of open-source AI contributions.
- American AI Labs - Beneficiaries of open-source AI contributions.
- Infrastructure Companies -